Daily Current Affairs : 14-December-2023
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has recently provided a captivating glimpse into the cosmic drama of a star’s explosive demise. The focal point of this astronomical spectacle is Cassiopeia A (Cas A), a supernova remnant that beckons us to explore its nature and origin.
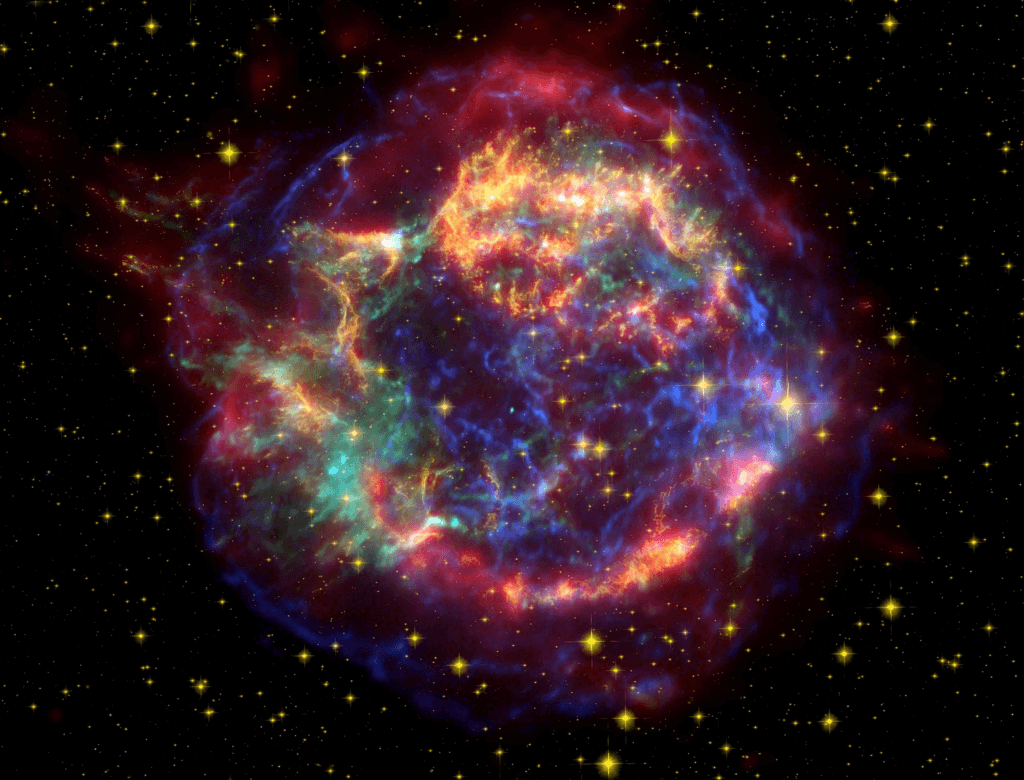
Cassiopeia A: Nature and Origin:
Cassiopeia A emerged from the cataclysmic explosion of a massive star around 340 years ago, making it the youngest known remnant of its kind in our galaxy. This celestial entity stands as a testament to the awe-inspiring forces at play in the cosmos.
Supernova Remnant Type:
Belonging to the prototypical category of supernova remnants, Cassiopeia A has been a subject of extensive study through various observatories. Researchers have delved into its formation and characteristics, unraveling the mysteries concealed within this celestial aftermath.
Spatial Dimensions:
Stretching across an impressive 10 light-years, Cassiopeia A occupies a significant expanse in the cosmos. Positioned 11,000 light-years away in the Cassiopeia constellation, its spatial presence enriches our comprehension of supernovae.
Scientific Insights from Cassiopeia A:
As a scientific treasure trove, Cassiopeia A provides invaluable insights into the complexities of supernovae phenomena. Exploring this remnant contributes significantly to our understanding of the intricate processes associated with massive star explosions.
Supernova Explosion: Unveiling the Cosmic Drama:
A supernova explosion, marking the grand finale of a massive star’s lifecycle, unfolds through fascinating scenarios.
- Binary Star System Scenario: In binary star systems, the drama unfolds as one star, often a carbon-oxygen white dwarf, accumulates matter from its companion. The culmination is a critical explosion, showcasing the breathtaking spectacle of a supernova.
- Single Star’s Culmination: Meanwhile, in the solitary journey of a single star, as it exhausts its nuclear fuel, mass flows into its core. Unable to withstand gravitational forces, the core collapses, triggering a colossal explosion—the hallmark of a supernova.
Important Points:
- Cassiopeia A: Nature and Origin:
- Remnant of a massive star’s explosive event 340 years ago.
- Youngest known remnant of its kind in our galaxy.
- Supernova Remnant Type:
- Prototypical supernova remnant category.
- Extensively studied for its formation and characteristics.
- Spatial Dimensions:
- Spans an impressive 10 light-years.
- Positioned 11,000 light-years away in the Cassiopeia constellation.
- Scientific Insights from Cassiopeia A:
- Rich source of information about supernovae phenomena.
- Contributes to unraveling complexities of massive star explosions.
- Supernova Explosion: Unveiling the Cosmic Drama:
- Binary Star System Scenario:
- Drama unfolds in binary star systems.
- Carbon-oxygen white dwarf accumulates matter, leading to a critical explosion—supernova.
- Single Star’s Culmination:
- Solitary star’s lifecycle finale involves mass flowing into the core.
- Core collapse results in a colossal explosion—the signature of a supernova.
- Binary Star System Scenario:
Why In News
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope captured a stunning new image of a star that exploded in the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A (Cas A), unveiling the intricate details of the celestial aftermath and providing valuable insights into the life cycle of massive stars.
MCQs about Cassiopeia A
-
What is Cassiopeia A?
A. A newly discovered planet
B. A prototypical supernova remnant
C. A distant galaxy
D. A binary star system
-
How long ago did the explosive event leading to Cassiopeia A’s formation occur?
A. 100 years
B. 340 years
C. 500 years
D. 1,000 years
-
Where is Cassiopeia A located in the cosmos?
A. 1,000 light-years away in the Orion constellation
B. 11,000 light-years away in the Cassiopeia constellation
C. 5,000 light-years away in the Andromeda galaxy
D. 8,000 light-years away in the Ursa Major constellation
-
What role does Cassiopeia A play in scientific exploration?
A. It’s a newly discovered celestial object.
B. It contributes to unraveling complexities of massive star explosions.
C. It’s a black hole at the center of our galaxy.
D. It serves as a distant galaxy for observation.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


